Opening hours: MO-FR from 09:00 - 18:00 (WE & public holiday closed)
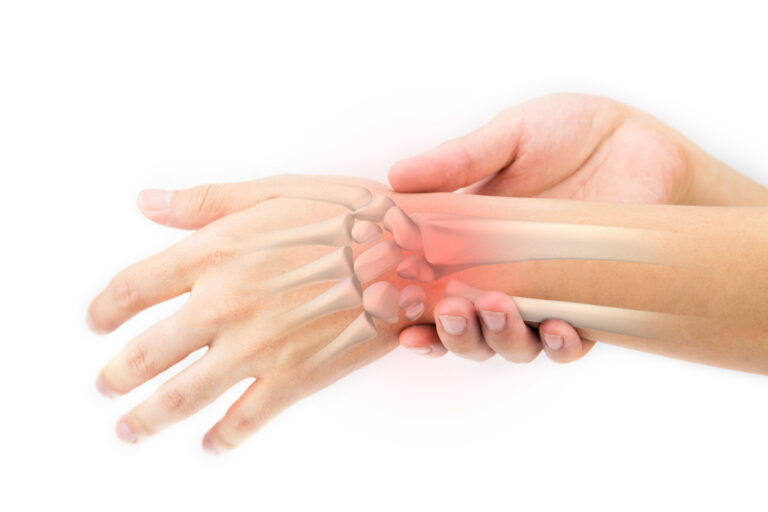
Carpal tunnel syndrome - numbness and tingling in the hand
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common nerve bottleneck syndrome in humans.
This leads to a constriction of the median nerve of the hand (median nerve) in the area of the wrist. At this point, the nerve runs together with the flexor tendons through a tunnel, which is bordered by the carpal bones and a wide ligament.
If a constriction occurs in this area, symptoms such as numbness, tingling and numbness occur, especially in the first to fourth finger of the affected hand. Burning, unpleasant pain can also occur.
These symptoms usually occur more frequently at night, causing those affected to wake up from sleep several times in order to alleviate the symptoms somewhat by shaking the hand. If the condition persists for a long time, it can also lead to muscular weakness and, as a result, to permanent degeneration of the muscles in the ball of the thumb.
In most cases, a suspected diagnosis can already be made when the patient is questioned in detail based on the specific symptoms. In addition, there are some special tests that can further confirm the suspected diagnosis when examining the hand.
Often a special X-ray and an ultrasound examination are also carried out. The final diagnosis is then made using electrophysiological measurements of nerve function, which are carried out by neurologists.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, there are several treatment options.
Mild symptoms can be treated primarily with conservative therapy. This involves the use of special night splints for the wrist. In addition, decongestant medication and, in some cases, local infiltration with cortisone injections may be useful.
If this non-surgical therapy fails, if the findings deteriorate or in the case of advanced carpal tunnel syndrome with incipient muscle weakness, prompt surgical treatment should be performed to prevent permanent damage.
The median nerve is surgically released from its constriction by cutting the rough ligament that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel.
The procedure can be performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia using a minimally invasive technique, is rarely associated with complications in experienced hands and in most cases leads to a rapid resolution of symptoms.